Chapter III Process
3.1 Process Flow Chart
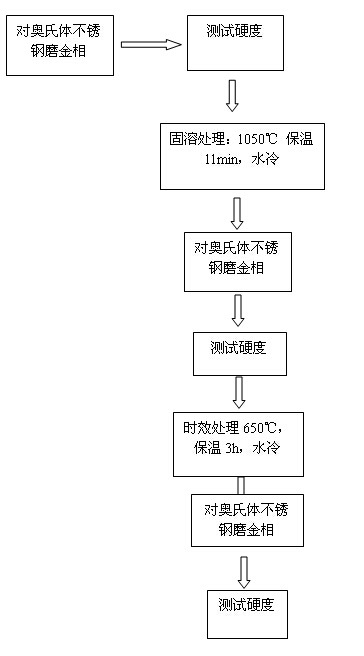
Figure 3-1
3.2 austenitic stainless steel grinding metallography
1. Grinding from coarse to fine sandpaper, it can be ground on the pre-grinding machine. From coarse sandpaper to fine sandpaper, change the sandpaper again. The sample must be rotated 90° to the vertical direction.
2. Pre-polished sample, first rough polishing on the polishing machine (• polishing fabric is fine flannel, polishing liquid is W2.5 diamond polishing paste), then fine polishing (polishing fabric is velvet, polishing liquid is W1.5 diamond polishing paste). When the wear scar on the sample is completely removed and the surface is mirror-finished, the roughness is Ra 0.04 or less.
3. The sample after fine polishing can be immersed in the etchant contained in the glass dish for etching. When etched, the sample may move slightly from time to time, but the polished surface shall not come into contact with the bottom of the dish.
4, metallographic microstructure inspection
3.3 hardness test
3.3.1 Notes
1. The test piece requires smoothness;
2. Understand the material and hardness range of the test piece and select the appropriate hardness scale;
3. Be careful when installing and removing the diamond to prevent it from falling. The test piece should be slow to contact the diamond to avoid damage or brittle diamond.
3.3.2 The operation steps are as follows
1. Adjust the loading speed of the main test force, place the handle in the unloading position, and turn the handle to the position of 1471N. Place the standard hard block of 35~55HRC on the workbench and rotate the handwheel to make the hardness block rise. The main shaft, plus the initial test force, pull the handle and add the main test force, observe the large pointer of the indicator, the time from the start to the stop should be in the range of 4 ~ 8s; if it does not match, you can turn the oil needle to adjust, repeat, until As appropriate.
2. When selecting the test force, turn the handle to align the selected test force with the red dot. It must be noted that when changing the test force, the handle must be placed in the unloaded state (ie the rear limit position).
3. When installing the indenter, care should be taken to eliminate the gap between the indenter and the end face of the spindle. The elimination method is: attaching the indenter and fixing it with screws, then placing the standard block or test piece on the worktable, rotating the hand wheel to add the initial test force, pulling the handle to apply the main test force to the pressure head, and then The screw can be tightened to eliminate the gap between the indenter and the end face of the spindle.
3.4 solution treatment
Solution treatment: 1050 ° C for 11 min, water-cooled (according to the empirical formula T = 1.5 h (T: holding time / min, h: thickness). Austenitic stainless steel softened by solution treatment, heating, holding for a period of time, carbonization The material and various alloying elements are uniformly and uniformly dissolved in austenite, and then rapidly quenched and cooled, carbon and other alloying elements are too late to precipitate, and a pure austenite structure is obtained, and the effect of solution treatment is 3 points.
1. Make the steel wire structure and composition uniform, which is especially important for raw materials, because the rolling temperature and cooling speed of each section of hot-rolled wire are different, resulting in inconsistent structure. At high temperatures, atomic activity is intensified, the σ phase dissolves, the chemical composition tends to be uniform, and a uniform single-phase structure is obtained after rapid cooling.
2, eliminate work hardening, in order to facilitate the continued cold processing. Through the solution treatment, the lattice recovery of the twist, the elongated and broken crystal grains recrystallize, the internal stress is eliminated, the tensile strength of the steel wire is lowered, and the elongation is increased.
3. Restore the inherent corrosion resistance of stainless steel. Due to the precipitation of carbides caused by cold working, the lattice defects cause the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel to decrease. After the solution treatment, the corrosion resistance of the steel wire is restored to an optimum state.
The reason why austenitic stainless steel has good corrosion resistance is that its substrate has a high electrode potential and is not susceptible to electrochemical corrosion, but usually after various thermal processing, a chromium-containing carbide is formed inside it: Cr23C6, which causes the content of chromium (n/8 regular) in the surrounding matrix to be greatly reduced, so that the electrode potential of the substrate is lowered, and the corrosion resistance is also greatly reduced. The purpose of the solution treatment is to eliminate the existing Cr23C6, it is re-dissolved into austenite to improve the corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steel [5].
3.5 aging treatment
Aging treatment at 650 ° C, holding for three hours, water cooling. In order to eliminate the change of size and shape of precision measuring tools or molds and parts in long-term use, the workpiece is often reheated to 100-150 °C after low temperature tempering (low temperature tempering temperature 150-250 °C). -20 hours, this process for stabilizing the quality of precision parts is called aging. It is especially important to aging the steel components under low temperature or dynamic load conditions to eliminate residual stress and stabilize the steel structure and size.
Austenitic stainless steel aging treatment Austenite grain boundaries after 650 aging include flat grain boundaries and serrated grain boundaries. M23C6 carbides precipitated on flat grain boundaries have the same characteristics as grain boundary carbides precipitated at 600 aging. The M23C6 carbide in the zigzag austenite grain boundary is parallel to the crystal grains on both sides [6].
Related information recommended:
Solid solution and aging of stainless steel - overview (1)
Solid solution and aging of stainless steel - testing equipment (2)
Solid solution and aging of stainless steel - process flow (3)
Solid solution and aging of stainless steel - test data and phase diagram (4)
Cotton Rope,Braided Cotton Rope,Macrame Cotton Rope,Macrame Rope
Baoying Yiliyuan Rope And Net Co.,Ltd , https://www.ylyropes.com